When a file is transfered into dCache its replica is copied into one of the pools. Since this is the only replica and normally the required range is higher (e.g., by default at least 2 and at most 3), this file will be replicated to other pools.
When some pools go down, the replica count for the files in these pools may fall below the valid range and these files will be replicated. Replicas of the file with replica count below the valid range and which need replication are called deficient replicas.
Later on some of the failed pools can come up and bring online more valid replicas. If there are too many replicas for some file these extra replicas are called redundant replicas and they will be “reduced”. Extra replicas will be deleted from pools.
The replica service counts the number of replicas for
each file in the pools which can be used online (see Pool States
below) and keeps the number of replicas within the valid range
(replica.limits.replicas.min, replica.limits.replicas.max).
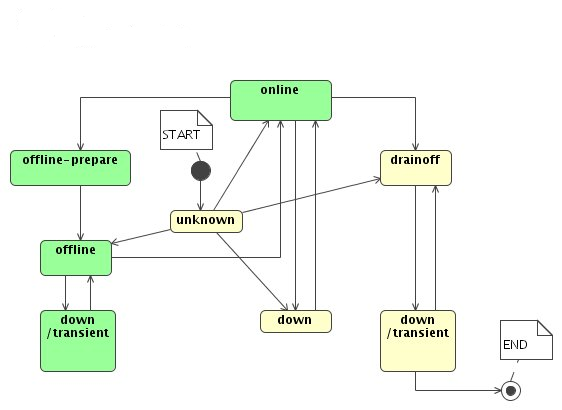
The possible states of a pool are online,
down, offline,
offline-prepare and
drainoff. They can be set by the admin
through the admin interface. (See the section called “Commands for the admin interface”.)
- online
Normal operation.
Replicas in this state are readable and can be counted. Files can be written (copied) to this pool.
- down
A pool can be
downbecause- the admin stopped the domain in which the pool was running.
- the admin set the state value via the admin interface.
- the pool crashed
To confirm that it is safe to turn pool down there is the command ls unique in the admin interface to check number of files which can be locked in this pool. (See the section called “Commands for the admin interface”.)
Replicas in pools which are
downare not counted, so when a pool crashes the number ofonlinereplicas for some files is reduced. The crash of a pool (pool departure) may trigger replication of multiple files.On startup, the pool comes briefly to the
onlinestate, and then it goesdownto do pool “Inventory” to cleanup files which broke when the pool crashed during transfer. When the pool comes online again, thereplicaservice will update the list of replicas in the pool and store it in the database.Pool recovery (arrival) may trigger massive deletion of file replicas, not necessarily in this pool.
- offline
The admin can set the pool state to be
offline. This state was introduced to avoid unnecessary massive replication if the operator wants to bring the pool down briefly without triggering massive replication.Replicas in this pool are counted, therefore it does not matter for replication purpose if an
offlinepool goes down or up.When a pool comes
onlinefrom anofflinestate replicas in the pool will be inventoried to make sure we know the real list of replicas in the pool.- offline-prepare
This is a transient state betweeen
onlineandoffline.The admin will set the pool state to be
offline-prepareif he wants to change the pool state and does not want to trigger massive replication.Unique files will be evacuated — at least one replica for each unique file will be copied out. It is unlikely that a file will be locked out when a single pool goes down as normally a few replicas are online. But when several pools go down or set drainoff or offline file lockout might happen.
Now the admin can set the pool state
offlineand thendownand no file replication will be triggered.- drainoff
This is a transient state betweeen
onlineanddown.The admin will set the pool state to be
drainoffif he needs to set a pool or a set of pools permanently out of operation and wants to make sure that there are no replicas “locked out”.Unique files will be evacuated — at least one replica for each unique file will be copied out. It is unlikely that a file will be locked out when a single pool goes down as normally a few replicas are online. But when several pools go down or set drainoff or offline file lockout might happen.
Now the admin can set the pool state down. Files from other pools might be replicated now, depending on the values of
replica.limits.replicas.minandreplica.limits.replicas.max.
When the replica service starts it cleans up the
database. Then it waits for some time to give a chance to most
of the pools in the system to connect. Otherwise unnecessary
massive replication would start. Currently this is implemented
by some delay to start adjustments to give the pools a chance
to connect.
Normally (during Cold Start) all information in the database
is cleaned up and recreated again by polling pools which are
online shortly after some minimum delay
after the replica service starts. The replica
service starts to track the pools’ state (pool up/down
messages and polling list of online pools) and updates the
list of replicas in the pools which came online. This
process lasts for about 10-15 minutes to make sure all pools
came up online and/or got connected. Pools which once get
connected to the replica service are in online or
down state.
It can be annoying to wait for some large period of time until all known “good” pools get connected. There is a “Hot Restart” option to accelerate the restart of the system after the crash of the head node.
On Hot Restart the replica service retrieves
information about the pools’ states before the crash from
the database and saves the pools’ states to some internal
structure. When a pool gets connected the replica
service checks the old pool state and registers the old
pool’s state in the database again if the state was
offline,
offline-prepare or
drainoff state. The replica
service also checks if the pool was
online before the crash. When all pools
which were online get connected once, the
replica service supposes it recovered its old
configuration and the replica service starts
adjustments. If some pools went down during the connection
process they were already accounted and adjustment would
take care of it.
Example:
Suppose we have ten pools in the system, where eight pools
were online and two were
offline before a crash. The
replica service does not care about the two
offline pools to get connected to start
adjustments. For the other eight pools which were
online, suppose one pool gets connected
and then it goes down while the other pools try to
connect. The replica service considers this pool in
known state, and when the other seven pools get connected
it can start adjustments and does not wait any more.
If the system was in equilibrium state before the crash,
the replica service may find some deficient
replicas because of the crashed pool and start replication
right away.
For security reasons you might want to spread your replicas
such that they are not on the same host, or in the same
building or even in the same town. To configure this you need
to set the tag.hostname label for your
pools and check the properties
replica.enable.check-pool-host and
replica.enable.same-host-replica.
Example:
We assume that some pools of your dCache are in Hamburg and some are in Berlin. In the layout files where the respective pools are defined you can set
[poolDomain]
[poolDomain/pool1]
name=pool1
path=/srv/dcache/p1
pool.size=500G
pool.wait-for-files=${path}/data
tag.hostname=Hamburgand
[poolDomain]
[poolDomain/pool2]
name=pool2
path=/srv/dcache/p2
pool.size=500G
pool.wait-for-files=${path}/data
tag.hostname=Berlin
By default the property
replica.enable.check-pool-host is
true and
replica.enable.same-host-replica is
false. This means that the
tag.hostname will be checked and the
replication to a pool with the same
tag.hostname is not allowed.
A hybrid dCache operates on a
combination of pools (maybe connected to tape) which are not
in a resilient pool group and the set of resilient pools. The
replica service takes care only of the subset of pools
configured in the pool group for resilient pools and ignores
all other pools.
Note
If a file in a resilient pool is marked precious and the pool were connected to a tape system, then it would be flushed to tape. Therefore, the pools in the resilient pool group are not allowed to be connected to tape.
If you are an advanced user, have proper privileges and you
know how to issue a command to the admin interface you may
connect to the ReplicaManager cell and issue the following
commands. You may find more commands in online help which are
for debug only — do not use them as they can stop
replica service operating properly.
- set pool <pool><state>
set pool state
- show pool <pool>
show pool state
- ls unique <pool>
Reports number of unique replicas in this pool.
- exclude <pnfsId>
exclude <pnfsId> from adjustments
- release <pnfsId>
removes transaction/
BADstatus for <pnfsId>- debug true | false
enable/disable DEBUG messages in the log file